
Cross Chain Bridge Explained
Cross chain bridge is a much needed solution in the cryptocurrency market. With such rapid developments taking place, restrictions cause more harm than good. Cross chain bridges are therefore established to tackle that.
In this article we well be glancing on the basics of cross-chain bridges and how cross-chain bridges are useful for investors and crypto enthusiasts.
What is a Cross Chain Bridge?
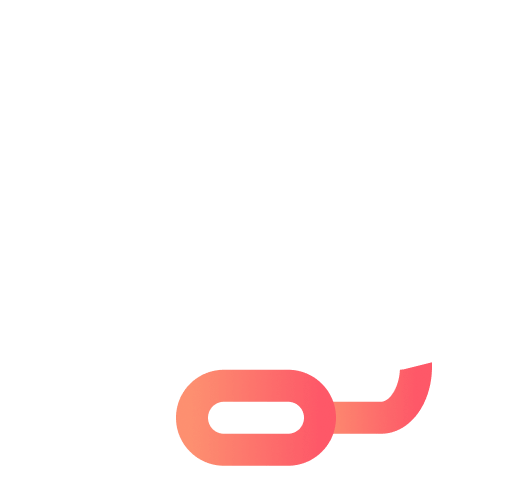
At its core, a cross-chain bridge, often referred to as a blockchain bridge, acts as a conduit between different cryptocurrencies, linking multiple blockchains together. These bridges serve as crucial infrastructure, empowering users to seamlessly transfer their digital assets across various blockchain networks. They provide a neutral ground for navigating the blockchain landscape.

Many cross-chain bridges in operation today primarily connect Ethereum with newly established blockchain networks. However, the latest generation of blockchain networks has already integrated cross-chain capabilities.
In practical terms, a cross-chain bridge allows users to effortlessly convert their holdings in one cryptocurrency into the equivalent amount in another cryptocurrency. It's akin to making a purchase in US dollars using Euros.
Advantages of Cross-Chain Bridge
A cross bridge can have several advatanges. Those can range from deploying token holdings to working as a middle man between different networks of a blockchain.

Other advantages include:
Increased productivity of assets:
Rather than letting their crypto assets lie dormant, users can leverage them for various purposes, such as using one asset as collateral for another. This strategy boosts the overall value generated by each asset.
Better User Experience:
Users are seeking services that prioritize speed, financial security, and swift transactions. Cross-chain bridges empower users to access enhanced features from one network while operating within another.
Use of DApps:
Decentralized applications (DApps) enable users to effortlessly move their funds across different blockchains, enhancing flexibility and functionality.
How do Cross Chain Bridges work?
The functionality of cross-chain bridges revolves around the generation and wrapping of different types of tokens. These tokens serve as reference values for the blockchain, creating receipts that can be employed on other networks.
For example, consider a scenario where you wish to transfer your token X holdings from Blockchain X to Blockchain Y. The bridge will take your token X holdings and generate an equivalent amount of token Y on Blockchain Y. This process does not entail transferring tokens from one blockchain to another; instead, it creates an equivalent amount of holdings on the destination blockchain using smart contracts.
These smart contracts are discarded when users move their token holdings back to the source blockchain.
Types of Cross-Chain Bridges
One of the cross chain bridges is Centralized, while the other one is Decentralized. The two categories are:
Trusted Bridges
Trusted bridges are centralized and designed for speed and affordability. However, they rely on a central organization, necessitating users' trust in a third party to facilitate the process effectively.
Trustless Bridges
Trustless bridges are decentralized and adhere to the standard procedures of blockchain networks. Users place their trust in the code that operates the bridge, making it more secure as it is immune to manipulation by centralized entities.
Conclusion
Cross-chain bridges are a remarkable innovation within the Web 3.0 landscape, facilitating connections between blockchain networks and enabling cross-chain transfers. They offer a much-needed convenience to users, fostering a more interconnected and versatile blockchain ecosystem.
As Web 3.0 continues to evolve, cross-chain bridges stand as a vital component, bridging the gap between the multitude of blockchain networks and ushering in a new era of digital connectivity.
(Click Here to Learn about Innovation Zone)
Image Credits: Zecrey; Li FI; China DeFi
