
What Is Proof Of Stake Mechanism In Blockchain?
Proof Of Stake (PoS) Explained
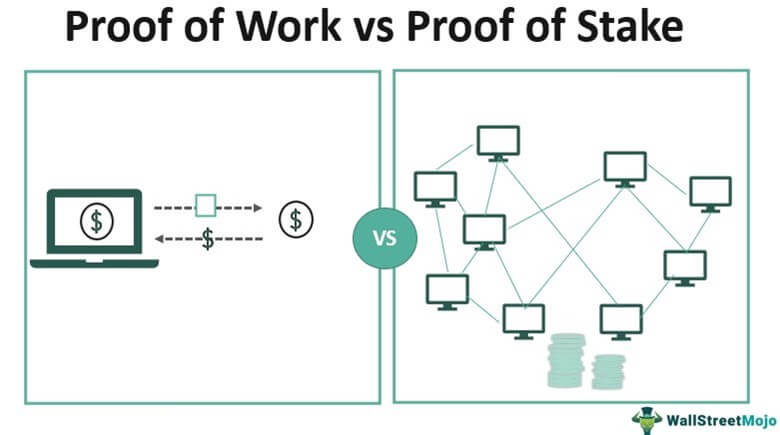
Proof of Stake (POS) is a consensus mechanism that diverges from Proof Of Work's (POW) energy-intensive race. Here, validators play a central role by staking their cryptocurrency as collateral to participate in the network.
Unlike Proof of Work, where anyone can join the network as a miner by owning tokens or coins, Proof of Stake introduces a cost to entry that grows as more participants join.
In Proof Of Stake, transparency reigns supreme. Validators' work is visible to all, ensuring the integrity of transactions and maintaining a valid blockchain.
To incentivize honest participation and penalize misconduct, Proof Of Stake introduces a concept known as 'slashing.' If a validator fails to validate a transaction due to issues like computer power or network lag, a portion of their staked coins is deducted.
Furthermore, any fraudulent activity, such as validating false transactions or self-transfers, results in the complete loss of their staked coins.
This security-first approach makes Proof Of Stake an attractive alternative to Proof Of Work, offering a shorter and more efficient race for block validation and enhanced scalability. Ethereum, one of the leading cryptocurrencies, is in the process of transitioning from PoW to PoS to address scalability issues and reduce its environmental footprint.
The PoS mechanism can be further categorised into the following:
Delegated PoS:
The main delegation can vote for others to be a delegator resulting in an easy democracy. Binance makes use of this mechanism.
Space and Time PoS:
It makes use of digital storage space and people get paid for storing data on their system. Filecoin and Bittorrent coins make use of this.
Proof of weight:
Technically the entire PoS mechanism can fall under it as it makes use of some weight value for eg. how many coins, duration of holding etc. to determine a validator.
Proof of authority:
It is a modified form of PoS where only a few nodes are trusted and those are not anonymous. It is centralised but also faster.
Proof Of Stake vs Proof of Work: How is Proof of Stake Different?
Both consensus mechanisms contribute to the synchronization, validation, and processing of data in blockchains. While each method has its advantages and disadvantages, they differ significantly in their approaches.
In Proof of Stake (PoS), validators are responsible for creating blocks. They verify transactions, assess activity, vote on outcomes, and maintain records.
On the other hand, in Proof of Work (PoW), miners create blocks by solving complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions. As a reward for solving these puzzles, miners receive a coin.
To participate as a block creator in PoS, one needs to possess enough coins or tokens to become a validator.
In PoW, miners must invest in processing equipment and bear substantial energy costs to power the machines involved in solving computations.
The expenses associated with equipment and energy in PoW make mining less accessible, thereby enhancing the blockchain's security.
In contrast, PoS mechanisms reduce the processing power required for validating blocks and transactions.
Additionally, they alleviate network congestion and eliminate the reward-based incentive seen in PoW blockchains.
Why is Proof of Stake Important?
PoS was developed to address network congestion and environmental concerns associated with PoW while remaining user-friendly.
Unlike PoW, where miners exchange energy for cryptocurrency, PoS randomizes an individual's mining ability, significantly reducing energy usage.
Ethereum's transition from PoW to PoS, for instance, led to a 99.84% reduction in energy consumption.
How is Proof of Stake secure?
Concerns about a 51% attack persist in cryptocurrency networks, including PoS. In PoW, this attack occurs when an entity controls over 50% of miners and manipulates the blockchain.
In PoS, an attacker would need to own 51% of the staked cryptocurrency, a costly endeavor.
Ethereum's PoS introduces a safeguard wherein honest validators can vote to disregard an altered blockchain and burn the staked ETH of the offenders in case of a 51% attack.
This incentive encourages validators to act honestly, bolstering cryptocurrency and network security.
In addition to these measures, PoS blockchains employ undisclosed security features to enhance their inherent security.
