
What is Crypto Mining? Explained
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of crypto mining, covering key factors, types, profitability of crypto mining, and potential risks and rewards.
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process in which new bitcoins are introduced into the transaction cycle. Moreover, it plays a crucial role in upkeeping and advancing the blockchain ledger.
Mining operates through a decentralized network of computers across the globe, working round-the-clock to verify and record transactions in a public ledger, known as the blockchain.
This process involves solving complex mathematical puzzles that require a high amount of computing power, thus the need for specialized hardware.
Once this “puzzle” is solved, the miner adds the 'block' of transactions to the blockchain, which is subsequently rewarded with bitcoin.
How does Bitcoin mining work?
Here's how Bitcoin mining works, step by step:

Verification
When someone sends bitcoins to someone else, the first thing miners do is check the transaction details to make sure it's legitimate. This involves making sure the sender actually owns the bitcoins they're trying to send.
Block Creation
Once transactions are verified, they are grouped into a 'block.' This is like a super complex math puzzle.
Solving the Puzzle
Miners are currently in a race to resolve this intricate problem. The one who manages to crack it first receives a prize. This 'solving' part of the mining process is actually guessing a 64-digit hexadecimal number (also known as a "hash") that needs to be less than or equal to the target hash. It's basically a race to find a number that fits the current puzzle.
Adding to the Blockchain
The miner who guesses the right number gets their block added to the blockchain. Once added, this block of transactions is visible to everyone who participates in the network.
(What is blockchain and how it works)
Reward
The lucky miner who guessed the right number is rewarded with some new bitcoins (this is called the "block reward") plus any transaction fees from the transactions included in their block.
It's important to note that the process consumes high energy due to the computational power required, particularly in the 'proof-of-work' stage.
Also, as the Bitcoin network grows and more transactions are processed, the mathematical problems that miners need to solve become more and more complex, requiring even more computational power.
What are the different types of crypto mining?
Cryptocurrency mining can be conducted in several ways. The method chosen typically depends on factors like cost, efficiency, and the miner's technical ability.
Here are the most common types of crypto mining:
- CPU Mining
- GPU Mining
- ASIC Mining
- Cloud Mining
- Mobile Mining
- Mining Pools
Let’s learn a bit more in detail about all of them individually.
What is CPU mining?
If you're wondering how to mine cryptocurrency on a PC without a GPU, CPU mining is the answer. CPU mining involves using the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to mine cryptocurrencies.
The process involves downloading a cryptocurrency client onto a computer and then using the CPU's processing power to solve complex mathematical problems, which validate transactions and secure the network.
CPU mining may not be as efficient as other forms of mining like GPU or ASIC mining because CPUs are designed to handle a wide variety of computer tasks and are not specialized for the kind of number crunching required in crypto mining.
However, CPU mining can still be profitable for some lesser-known altcoins, and it remains a feasible entry point for individuals who want to get started with mining but do not have the resources for more advanced mining hardware.

What are the best CPU Mining coins?
Monero (XMR) is the most profitable coin to mine on a CPU mining setup according to an article by PCGuide
What are the best cpu mining softwares?
EasyMiner, MultiMiner and CGMiner are quite popular options amongst crypto miners.
What is GPU mining?
GPU mining involves using the processing power of a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) found in a computer's graphics card to mine cryptocurrencies. GPUs are efficient at performing parallel computations, making them ideal for the complex calculations required in mining.
Miners use specialized software to utilize multiple GPUs simultaneously, achieving higher hash rates and computational performance compared to CPU mining. GPUs are more powerful and versatile, allowing miners to switch between different coins based on profitability.
However, GPU mining requires a significant investment in high-performance GPUs and consumes substantial electricity. It faces increased competition as more miners enter the space, making profitability more challenging.
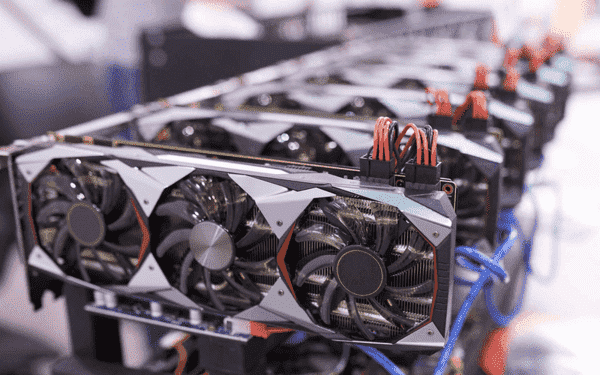
Despite challenges, GPU mining remains popular due to its efficiency and flexibility. It is favoured for coins resistant to ASIC mining or those suitable for GPU mining algorithms.
In summary, GPU mining harnesses graphics card power for cryptocurrency mining, offering higher performance than CPUs. It demands investment and energy consumption but provides efficiency and versatility.
Remember, mining can negatively impact your GPU as it generates significant heat, a side effect of the process. If you consistently operate your mining system around the clock at elevated temperatures - exceeding 80C or 90C - this could cause harm to the GPU, substantially reducing its operational life as per this article from gfinity. It is safe to mine with GPU as long as you know what you’re doing.
What are some of the most profitable GPUs for mining?
Profitability of GPU mining depends on various factors like location, cost of GPUs, etc. So here are our top 5 picks for the most profitable GPUs for mining.
(P.S. all of the price data have been noted down from amazon.com)
1. Nvidia GeForce RTX 3080
Power Consumption: 350 Watts
Hashrate: 125 MH/s
The cheapest non-LHR (Low Hash Rate) variant we found on Amazon at the time of writing was for USD $999
2. AMD Radeon RX 5700 XT
Power Consumption: 225 Watts
Hashrate: 54 MH/s
The cheapest 5700 XT we found on Amazon at the time of writing was for USD $399
3. Nvidia GeForce GTX 1080 Ti
Power Consumption: 213 Watts
Hashrate: 34 MH/s
The cheapest 1080Ti we found on Amazon at the time of writing was for USD $275
4. AMD RX 6800
Power Consumption: 145 Watts
Hashrate: 32 MH/s
The cheapest RX 6800 we found on Amazon at the time of writing was for USD $510
5. Nvidia GeForce RTX 2070
Power Consumption: 225 Watts
Hashrate: 36 MH/s
The cheapest RTX 2070 we found on Amazon at the time of writing was for USD $499.
What is ASIC mining?
ASIC mining refers to the use of specialized hardware called Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) to mine cryptocurrencies. ASICs are designed solely for mining specific cryptocurrencies and are highly optimized for efficiency.
Unlike general-purpose CPUs or GPUs, ASICs offer significantly higher hash rates and computational power. They are specifically tailored to handle the hashing algorithms used by certain cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin and Litecoin.
However, ASIC mining has limitations. ASICs are not versatile and cannot be easily reprogrammed for different coins or algorithms.
They can become obsolete if the targeted cryptocurrency changes its algorithm or if newer, more advanced ASIC models are introduced.
ASIC mining hardware tends to be expensive and is often dominated by large-scale mining operations due to the specialized nature and high competition.
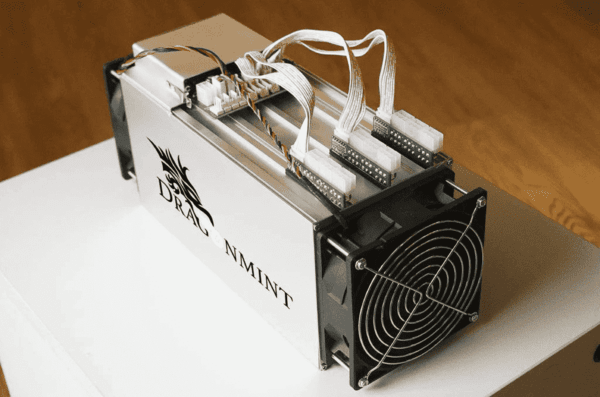
How do ASIC miners work?
ASIC miners work by utilizing specialized hardware called Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) to perform the computational tasks required for cryptocurrency mining. Here's a brief explanation of how ASIC miners operate:
ASIC Design:
ASIC miners are custom-built integrated circuits designed specifically for mining cryptocurrencies. The design process involves optimizing the hardware architecture to efficiently perform the specific hashing algorithms used by the targeted cryptocurrency.
Efficiency and Performance:
ASIC miners are highly efficient and powerful due to their specialized design. They are capable of performing a massive number of hash calculations per second, significantly surpassing the computational capabilities of general-purpose CPUs or GPUs.
Hashing Algorithms
Each cryptocurrency utilizes its own hashing algorithm, such as SHA-256 for Bitcoin. ASIC miners are engineered to execute these specific algorithms with exceptional speed and efficiency, maximizing their mining potential.
Dedicated Hardware
ASIC miners consist of dedicated hardware components, including the ASIC chips, power management systems, cooling mechanisms, and interfaces for connectivity and control.
Mining Software Integration
ASIC miners require compatible mining software to configure and control their operations. The software allows miners to connect to mining pools, track performance, and adjust mining parameters.
Network Participation:
Once set up and connected to the mining software, ASIC miners join the cryptocurrency network. They receive mining jobs from the mining pool or directly from the network, including a list of transactions to verify and a target value to find a hash that meets the required criteria.
Hashing Process
ASIC miners perform repeated calculations, using their immense computational power to find a specific hash value that fulfils the mining requirements. This process involves iterating through various combinations until a valid hash is discovered, which results in the successful mining of a new block.
Is ASIC mining profitable?
When power is inexpensive and the equipment is effective, mining bitcoins can be profitable. While shifts in mining hash rates are unquestionably driven by demand and pricing, the profitability of mining is also contingent on the value of a particular cryptocurrency.
It may or may not be lucrative depending on the economics of a particular blockchain and coin. It may be mined profitably using a mining pool. You can simply assess the profitability of ASIC mining for a certain cryptocurrency using online calculators.
What is Crypto Cloud Mining?
Cloud mining refers to a mining method where individuals or organizations rent mining resources from third-party providers. Instead of purchasing and maintaining physical mining hardware, users pay for a share of the mining power provided by the cloud mining service.

How does cloud mining work?
Service Provider
Cloud mining involves partnering with a cloud mining service provider. These companies own and maintain mining hardware in their data centers. They handle the setup, maintenance, and operation of the mining equipment.
Contract Selection
You choose a cloud mining contract that suits your needs. Contracts typically vary in duration and the amount of hashing power allocated to you. The hashing power determines your mining output.
Mining Allocation
Once you've purchased a contract, the service provider allocates a portion of their mining hardware's computational power to your account. This allows you to participate in the mining process without physically owning the hardware.
Remote Mining
The mining equipment in the data center, which may include ASIC miners or GPUs, is connected to the mining pool or the blockchain network. It performs the necessary calculations to validate transactions and mine new blocks.
Mining Rewards
As a cloud mining customer, you receive a share of the mining rewards proportional to the amount of hashing power you've allocated. The service provider handles the distribution of rewards.
Maintenance and Fees
The cloud mining service provider takes care of hardware maintenance, electricity costs, cooling, and other operational expenses. They deduct fees from your mining earnings to cover these costs.
Here are some of the popular cloud mining sites
1. IQ Mining
2. HashShiny
3. Hashing24
4. ECOS
5. Crypto Universe
How to avoid cloud mining scams?
While cloud mining seems like a convenient way to crypto mining, it is important to be aware of potential scams and fraudulent operations. Here are some common scams associated with cloud mining:
Fake Cloud Mining Providers
Scammers may set up websites posing as legitimate cloud mining providers. They entice users with attractive offers, promising high returns and low fees. However, once users invest and purchase mining contracts, the scammers disappear, leaving victims with no mining services or returns.
Ponzi Schemes
Ponzi schemes operate by using the money gathered from recent participants to provide payouts to those who invested earlier. Some cloud mining operations operate as Ponzi schemes, promising high returns but relying on a constant influx of new investors to sustain payouts. Eventually, the scheme collapses when new investors dwindle, resulting in financial losses for participants.
(Read our blog about Ponzi Schemes)
Unverifiable Mining Operations
Some cloud mining providers claim to have vast mining facilities but do not provide any verifiable proof of their mining operations. They may offer limited transparency and lack evidence to support their claims of mining activity, making it difficult to determine if the service is legitimate.
Hidden Fees and Unfair Terms
Scammers may include hidden fees or unfair terms in their mining contracts. They might impose exorbitant maintenance fees or charge high withdrawal fees, significantly reducing the profitability of the mining operation.
Difficulty Adjustments and Lack of Transparency
In genuine cloud mining, mining rewards are influenced by the difficulty of the cryptocurrency network. Scammers may manipulate difficulty levels or lack transparency in sharing mining statistics and details, making it difficult for users to verify the legitimacy of the operation.
To avoid falling victim to cloud mining scams, it is crucial to conduct thorough research and due diligence:
- Research the cloud mining provider and check for reviews and user experiences.
- Look for proofs, such as photos or videos of the mining facility.
- Evaluate the terms and conditions of the mining contracts, including fees and payout structures.
- Be cautious of unrealistic promises and overly high returns.
- Use reputable and established cloud mining providers with a track record of reliability.
By being vigilant and taking necessary precautions, individuals can minimize the risks associated with cloud mining and avoid falling prey to scams.
Is Cloud Mining actually profitable?
Cloud mining might be profitable, but the profitability depends on a variety of factors, and it's important to approach it with caution due to the associated risks.
It is possible to make a profit from cloud mining under the right circumstances. If you're thinking about trying out cloud mining, here are some factors to keep in mind:
Cryptocurrency Value
If the price of the cryptocurrency you're mining increases, your profits can also increase, assuming all other variables stay the same.

Mining Difficulty
Cryptocurrency mining tends to get more difficult over time as more miners join the network. This can decrease the amount of cryptocurrency earned from mining, reducing profitability.
Contract Terms
Cloud mining companies often sell contracts that dictate how much computing power you're leasing and for how long. These contracts also stipulate fees for maintenance and electricity. Make sure you fully understand these terms and calculate whether you can still make a profit after these costs.
Legitimacy of the Cloud Mining Operation
There are many fraudulent companies in the cloud mining industry. Do your research to ensure the company is legitimate before investing.
Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency prices are highly volatile. If the price drops significantly, your mining operation could become unprofitable.
Remember, although it's possible for cloud mining to be profitable, it can also involve significant risk. It's important to do thorough research and consider whether you're comfortable with the potential for losing your investment before you proceed.
What is a Mining Pool?
Cryptocurrency mining can be a tough challenge for solo miners due to its energy-intensive nature and the high level of computational power required. This is where mining pools shine.
A mining pool is essentially a collective of cryptocurrency miners who amalgamate their computing power over a network.
Instead of mining individually, they work together to solve complex mathematical problems involved in validating transactions and creating new blocks in the blockchain.
When a miner from the pool successfully mines a block, the reward is shared among all miners in the pool proportional to their contributed computing power.
ASIC vs GPU mining
ASIC and GPU are two types of hardware commonly used for cryptocurrency mining. They have some key differences.

ASIC Mining
Purpose-Built:
ASICs are designed for a specific use case - in this case, mining a specific cryptocurrency. They are incredibly efficient at performing the calculations required to mine that particular currency.
High Performance:
ASIC miners are much faster and more power-efficient when mining the specific cryptocurrency they were designed to mine.
Less Flexibility:
ASICs can only mine cryptocurrencies that use the same mining algorithm for which the ASIC was designed. If a cryptocurrency changes its mining algorithm, or if you want to switch to a different coin that uses a different algorithm, the ASIC could become useless.
Centralization Concerns:
Since ASICs are expensive and not universally accessible, their use can lead to centralization, with a small number of entities controlling a large proportion of the mining power.
GPU Mining
General Purpose:
GPUs are designed for visual rendering purposes, such as video gaming and graphics design, but they can also be used for mining cryptocurrencies which makes them more flexible than ASICs.
Lower Performance
For the specific task of mining cryptocurrencies, GPUs are generally slower and less power-efficient than ASICs. However, they can still be profitable, especially when mining coins that are not yet supported by ASICs or are resistant to ASIC mining.
More Flexibility
GPUs can mine any cryptocurrency that is mineable, providing more flexibility if a miner decides to switch the cryptocurrency they are mining.
Decentralization
GPUs are more widely available and affordable than ASICs, leading to greater decentralization in mining.
CPU vs GPU Mining
Cryptocurrency mining involves performing complex calculations to validate transactions and add them to a blockchain. Different hardwares can be used for this process, with the two most common types being CPUs and GPUs. Here's how they compare.
CPU Mining
Versatility
CPUs are extremely versatile and can handle a variety of tasks. They are capable of mining any coin, although the rate at which they mine might not be efficient.
Less Power
CPUs typically have fewer cores and operate at slower speeds than GPUs. This means they are less powerful when it comes to mining cryptocurrencies, which requires a lot of processing power.
More Energy Use per Computation
Because CPUs are less efficient at performing the types of calculations required for cryptocurrency mining, they tend to use more energy per hash (unit of mining computation) than GPUs or ASICs.
Accessibility
CPUs are a component of every computer, meaning anyone with a computer can start CPU mining without making any additional investment in hardware.
GPU Mining
Specialization
GPUs are designed to be amazing at performing certain types of calculations. Specifically, they are excellent at the type of repetitive, parallelizable calculations required for both rendering graphics (their primary design use) and mining cryptocurrencies.
More Power
GPUs typically have more cores and can handle more calculations per second than a CPU. This makes them much more effective at mining cryptocurrencies.
Efficiency
GPUs are more power-efficient for mining purposes than CPUs. They can perform more calculations for the same amount of power, which can lead to lower electricity costs and better overall profitability.
Versatility
GPUs are not as versatile as CPUs in terms of the overall variety of tasks they can handle. However, they can mine a broader range of coins efficiently compared to ASIC miners, which are another type of mining hardware that's even more specialized than GPUs.
In summary, while it's technically possible to mine with both CPUs and GPUs, GPUs are generally much more effective and efficient for mining purposes.
CPUs have largely been rendered obsolete for most popular cryptocurrencies due to their lower computational capability and higher energy usage per hash.
However, they might still be used for certain less computationally-intensive cryptocurrencies.
Now let’s get started on how one starts crypto mining.
How to start crypto mining?
Before you start your crypto mining journey, these are 3 things that you will need to start the crypto mining process:
1. Crypto wallet
2. Mining Software
3. Mining Hardware
Crypto wallet
You will need a crypto wallet to store all of your mined coins which also supports storing your specific mined coin.
There are a lot of wallets available online, and there are also some that even exist in the form of "cold storage" wallets, which function offline. It's crucial to determine the type of wallet that best suits your requirements prior to initiating your mining process.
Mining Software
You'll need to download mining software compatible with your hardware and the cryptocurrency you've chosen. While most mining softwares are free, here are some of the popular mining softwares:
1.CGMiner
2.EasyMiner
3.HoneyMiner.
Mining Hardware
Now comes the most- pocket-burning part of crypto mining, deciding on the hardware. Based on your budget, you’ll need to build a powerful crypto-mining rig.
How much does a Crypto Mining Rig cost?
Whenever you buy or build a crypto mining rig, just remember that more hash rate means more profitability or more mining rewards.
Just like we discussed above about the different types of mining, your most money-draining part of crypto mining would be a hardware, you could decide between getting an ASIC as discussed above or you could get a home computer with a powerful CPU and a GPU.
The Bitmain Decred Miner DR5 which is an ASIC costs roughly $5,600 which would mine around 35 terahashes per second (TH/s). You could also go for the Bitcoin Miner S10 Pro which mines at 110TH/s.
If you decide on going the home computer route, your main focus would ideally be towards the GPU and a good GPU for mining would be an RTX 3090 Ti which costs about $1,700 and mines at 133 mega hashes per second (MH/s). You could also have multiple GPUs in your Home Computer turned crypto mining rig.
What is Bitcoin Hashrate?
The hashrate is the speed at which a miner's hardware is making operations in the Bitcoin code, aiming to solve a complex mathematical problem that leads to block creation in the Bitcoin blockchain.

It's a measure of the miner's computational power. Higher hash rates mean more hashes a miner can perform per second, and the higher the chances of solving the mathematical problem, thus mining a new block and receiving the Bitcoin reward.
How long does it take to mine 1 Bitcoin?
It can take about 10 minutes to even 30 days to mine a single bitcoin according to this article by Techslang.
Can I mine Bitcoin on my phone?
Yes, it is possible to mine Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies on your phone, here are some of the popular crypto mining apps for both Android phones and iPhones:
- Storm Gain
- Crypto Tab
- BitDeer
- ECOS
- CoinX

Disadvantages of crypto mining apps
Limited Processing Power:
Mining cryptocurrencies requires a lot of processing power. Smartphones, while powerful for everyday tasks, are not designed for the kind of computational work required in mining.
Battery Life:
Mining uses a lot of energy and can drain a smartphone's battery quickly, reducing its lifespan.
Overheating:
The continuous heavy processing load put on the smartphone by mining can lead to overheating, which could damage the phone.
Economic Feasibility:
The amount of cryptocurrency you can mine with a smartphone is usually very small and likely won't cover the costs of electricity used, let alone the wear and tear on your device.
Taxes on Crypto Mining
Yes, your rewards from crypto mining can be taxed and the interest and process vary from country to country.
If you are a US citizen, you will be taxed twice:
1. Income tax on the mining rewards when mined
2. Capital gains taxes when you sell the mining rewards
In case the value of your mining rewards drops, you can take the benefit of loss harvesting to lower capital gains taxes.
If you are from Australia, you don’t need to pay taxes on your mined coins if you’re mining as a hobby, you will only be liable to pay taxes on capital gains when you sell/trade them.
But if you are a business miner, you are liable to pay taxes on your income rewards from mining as well as capital gains when you decide to sell your mining rewards.
Canadian miners are liable to pay capital gains and not income tax from mining rewards if they are doing it as a part of their hobby as same as that in Australia,
If you use a home computer to mine in the UK, you’re quite likely to be a hobby miner. As a hobby crypto-miner in the UK, you’ll pay income tax on your mined rewards in GBP as well as pay capital gains tax when you sell your mining rewards.
But if your crypto mining operations are classified as business, mining rewards will be added to your trading profits and be considered capital gains. You will also pay capital gains tax when you decide to sell/trade them.
If you are from India, you’ll pay 30% tax on your profits from trading crypto as well as 1% TDS if the sale exceeds Rs 50,000 in a single financial year. You are also liable to pay income tax on your mining rewards.
Conclusion
Crypto mining has grown exponentially, attracting both enthusiasts & professionals to this decentralised ecosystem.
As the mining industry becomes more competitive and resource-intensive, miners must adopt sustainable practices that reduce energy consumption, promote environmentally friendly alternatives, and remain profitable in doing so.
All future participants in this space must conduct extensive research and understand the risks associated with cryptocurrency mining. With careful consideration, one can choose to stay away from this exciting field or participate in it and potentially reap the benefits it provides.
If you liked our article, Check out our other article on Perpetual Contracts.
Check out our article on Bitcoin ETFs.
Also Read: What is PYUSD?
Image Credits: Coin ledger; Crypto Browser; crypto miners ae; Howtostartanllc.com; Coin Topper; coinmarketcap; coindesk; Appauls; buybitcoinworldwide; Atomic Wallet.
