
What are Blockchain Forks? Explained!
Blockchain forks serve as crucial updates in the world of blockchain technology. In essence, they are modifications that refine the blockchain's operations and enhance its utility.
Blockchain, as a decentralized and distributed system, records all transactions while maintaining transparency among users.
However, like any technology, it requires updates and adjustments to remain relevant and secure. These essential modifications are executed through a process known as forking.
What are Forks in Blockchain?
Blockchain forks are essential updates that tweak the blockchain's operations, leading to improvements in its functionality and usage like done in the Cardano Hardfork.
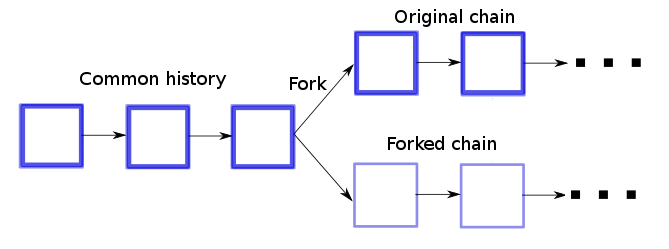
To better grasp the concept of forking in blockchain, let's draw a parallel with computer code. Much like computer codes necessitate regular updates for optimal performance, bug removal, and enhanced features, blockchains require periodic adjustments.
These updates address issues such as bug fixes, security enhancements, and the addition of new features, ensuring that the blockchain remains a robust and reliable technology.
One distinguishing aspect of blockchain forks is their decentralization. Unlike centralized systems where updates are mandatory for all users, in a decentralized blockchain network, individuals have the autonomy to choose whether they want to transition to the forked chain or continue using the original one.
Types of Forks
Blockchain forks are broadly categorized into two main types: soft forks and hard forks. Each type carries distinct implications and consequences.
Soft Crypto Fork
A soft fork represents an update that does not fully alter the blockchain protocol. Instead, it is introduced to address minor issues or bugs, making it backward compatible. In other words, even with the introduction of new changes, the blockchain can still function with older versions. Soft forks are often employed for minor improvements that do not fundamentally change the protocol.
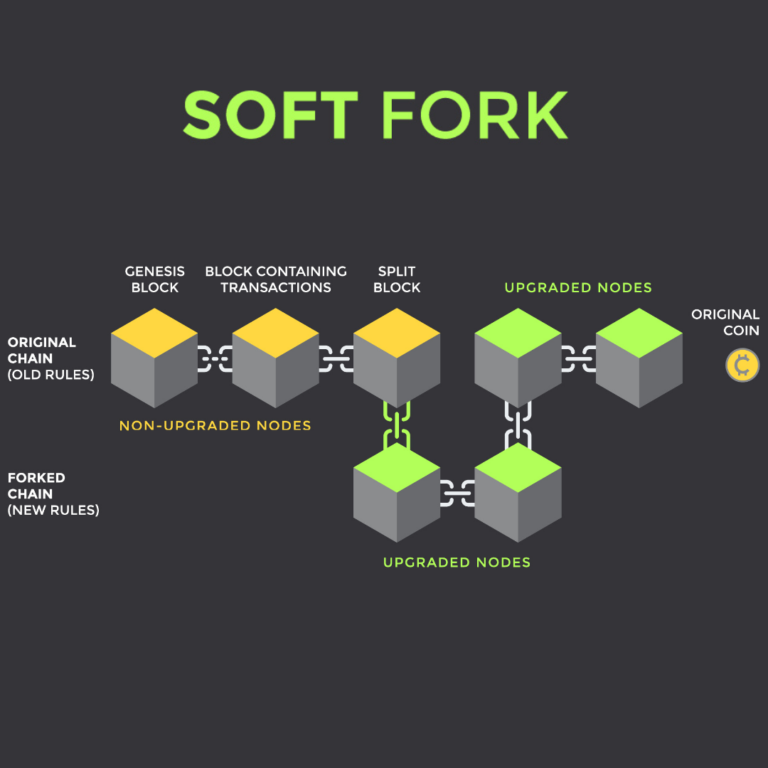
However, the advantage of being backward compatible comes with limitations. Soft forks cannot introduce substantial changes or alter the core principles of the blockchain's protocol, as this would compromise backward compatibility.
Hard Crypto Fork
In contrast, hard forks are updates that are not backward compatible, necessitating immediate adoption by blockchain users. Hard forks are designed to make substantial alterations to the blockchain's protocols and introduce significant changes to the technology's operation.

Let’s take an example for a better understanding. In the case of Bitcoin, which operates on the Bitcoin blockchain, any desire to enhance efficiency or resolve critical issues would lead to the introduction of hard forks. Consequently, the blockchain would split into separate chains, with each chain following its distinct set of rules within the Bitcoin protocol.
Listed below are some FAQs related to blockchain forks:
If we update the hard fork and accept it, it will change the protocol. Now, what will happen to our coins?
Ans- Assume that you have somewhere close to 2 Bitcoins before the bitcoin hard forks was introduced. Now, when you update the Bitcoin protocol, you will still have the 2 Bitcoins plus, you will also get the same amount of the other coin in the separated chain.
If everyone has double the number of coins they own. What will happen to the price?
Ans- We all know that the crypto market depends on the supply and demand procedure; thus, when the two separate chains are formed after the hard fork, the coin's pricing depends on whether the market believes that the two coins will survive or not.
When the blocks of a cryptocurrency split, what happens to their original name?
Ans- Yes, both the separate chains originate from the same user base and share the same past, but they are not the same anymore, they act as separate chains and thus, they have different names. For example, the older version of the Ethereum Blockchain is known as Ethereum Classic.
Conclusion
As blockchain technology continues to advance, so does the concept of blockchain forks. The future may witness contentious hard forks driven by diverse opinions on blockchain direction, as well as efficient soft forks aimed at introducing improvements with minimal disruption. The need for significant updates or enhancements will persist, ensuring the ongoing relevance of blockchain forks in the ever-evolving ecosystem.
In conclusion, blockchain forks play a pivotal role in the dynamic blockchain landscape. They are essential for executing updates, bug fixes, and improvements in the blockchain, whether through a soft or hard fork. While opinions on forks may vary, they remain a critical innovation that promises a promising future, albeit with a few bumps along the way.
(Also read: Hyperledger Consensus Mechanism)
Image Credits: Coinomi; bitcoin.tax; ByBit.
