
All About Polygon 'zkEVM'
The logo of Polygon might be a hexagon but it comprises seven different teams who build an interrelated web of products. Out of these seven teams, three teams i.e. Hermez, Zero, and Maiden have been working together to scale Ethereum with zero-knowledge-based tech.
Polygon believes that zero-knowledge tech is the most promising way to scale Ethereum as this tech shall be able to provide us with the scalability in the ZK Proofs and compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine or EVM.
What is Zero Knowledge Proof?
We have been reading a lot in this article about zero-knowledge-based tech, but what is it all about?
When it comes to choosing Ethereum Scaling solutions, the web developers have various options from the Layer 12 improvements like Ethereum 2.0 to the Layer 2 chains like Optimism and Arbitrum but still, they prefer to choose ZK Rollups, why?
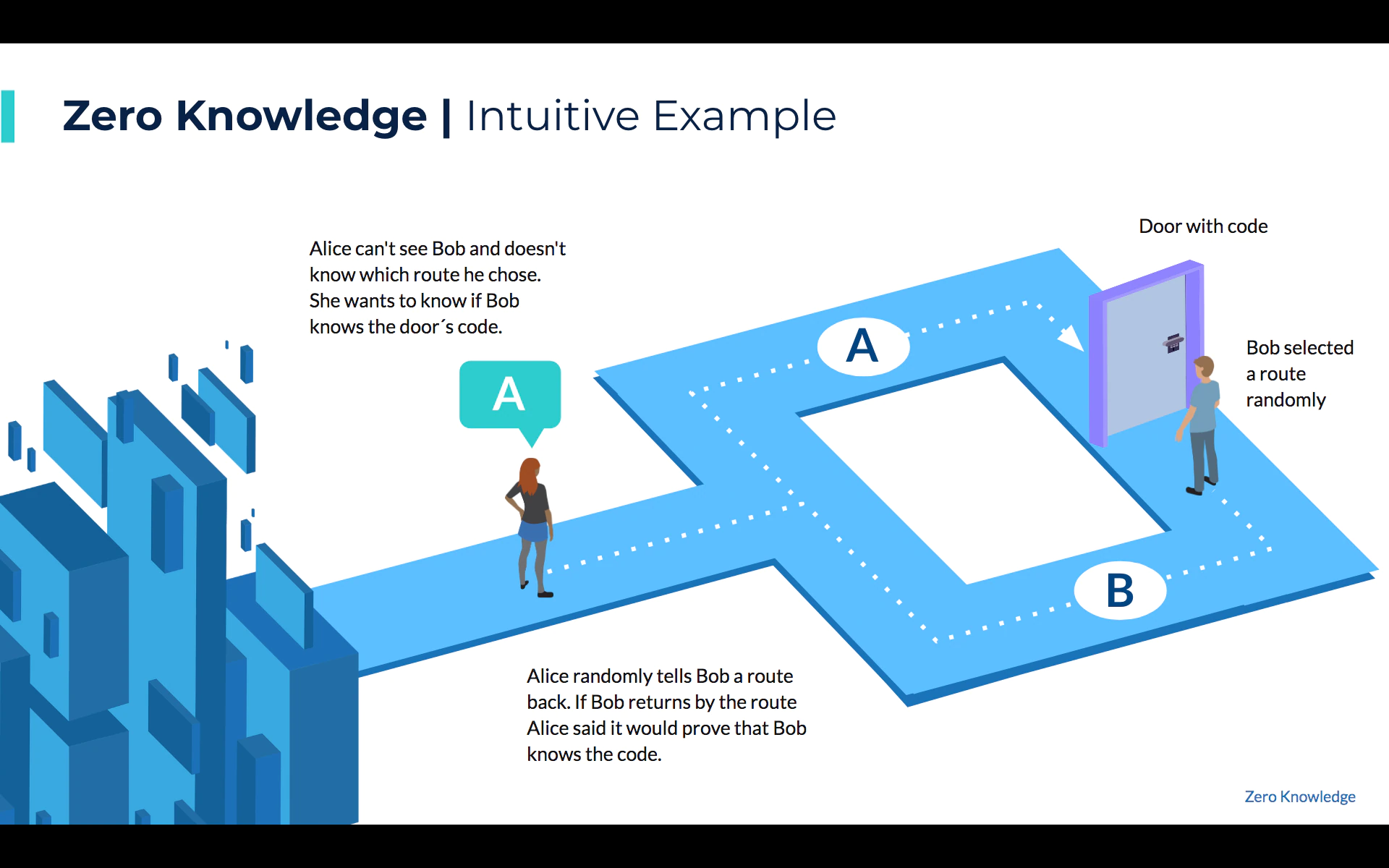
To explain zero-knowledge tech in simple words let us concentrate on its name. As the name suggests, the zero-knowledge proof is a cryptographic technique in which no information is shared or revealed during a transaction over the blockchain network.
With the increasing trend of fraud among various crypto transactions, zero-knowledge tech is a very simple yet very efficient way to minimize these frauds over blockchain technology. Thus, this is the reason why the teams at Polygon believe that zero-knowledge proof would be the best way to scale Ethereum in a sustainable manner.
What is a zkEVM?
A zkEVM is an advanced virtual machine that works on zero-knowledge proof tech which makes it more secure than usual. Unlike regular virtual machines, a zkEVM proves and validates the input and output of every transaction made without actually revealing the whole activity on the server.

To get a better understanding of how the zkEVM works and how is this better than the regular EVM let us take a quick look at what an EVM does and how it works:
What does the regular EVM do?
To understand the working of an EVM, let us consider a situation of a peer-to-peer transaction being conducted between two investors.
1- The regular EVM will act in such a way that at first, all the contract bycodes will be compiled from the source and uploaded to the EVM storage from where the peer-to-peer nodes will be executed. The nodes will use the same transaction inputs to ensure they reach the correct destination
2- Now, the EVM Opcodes will interact with different states of the EVM i.e. Memory, storage, and stack, and thus will read the values from state storage and then send the new values to the EVM's storage.
3- And finally, these new states of values will be replicated by the new nodes and will be sustained until another transaction is carried out.
This was a standard working of an EVM at the time of executing transactions. Now, what does the zkEVM have in store for us?
zkEVM is kind of a modified version of the EVM which works more or less like the EVM but with better security and faster speed.
What does a zkEVM do that it becomes better than the regular virtual machines? Let's have a look.
The zkEVM generates zero-knowledge proof to verify all the elements during each transaction revealing no information to the network which makes it way more secure than regular virtual machines. The zk rollups upload the validity proof over the Ethereum blockchain instead of all the details of the transaction reducing the risk of frauds and maintaining transparency during the peer-to-peer transactions.

Now we all know how the zkEVM works and how it is better than the regular EVMs, but there are many difficulties associated with it too. As the regular virtual machines were not built to implement the zk-proofs, thus, it still has some features that are unfriendly and make building zkEVMs difficult. Some of these problems are listed below:
1: Unlike a regular virtual machine, the EVMs use Special Opcodes for program execution and to execute zk-proofs. This adds complexity to the process of designing the proving circuit over the network.
2: Because these virtual machines were never made keeping zero-proof technology in mind and generating zero-proof knowledge requires specialized hardwares along with a considerable amount of money and their resources to invest in it too. This is what presents some problems and hampers the efforts to build zero-knowledge based virtual machines.
3: Lastly, the architecture for both EVMs and zkEVMs is also different. On one hand, the zkEVMs use register-based architecture which is a modified version of stack-based architecture used by the regular EVMs. (stack based architecture is a list of data words while register-based architecture makes use of general-purpose registers which can consist of any mathematical operand)
The stack-based architecture is a very simple one in comparison to register-based architecture.
Conclusion
This was a brief view of the Polygon zkEVM over the Ethereum blockchain which is a much faster and more secured way of proceeding with the transactions over the blockchain technology. The zkEVM is the modified version of the regular virtual machines but it executes the transactions without revealing any information over the network.
The Polygon zkEVM was built by Polygon but it can be used by everyone who needs a better, cheaper and much faster way to use Ethereum without sacrificing their security or decentralization.
(Click here to learn about The Different Types of Blockchain)
